Morphological Comparative Changes in Skin Healing by Using Postbiotic Cream and Antibiotics in Rabbit
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59675/V316Keywords:
Postbiotic cicalfate+ cream, penicillin-streptomycin, wound healing, rabbits.Abstract
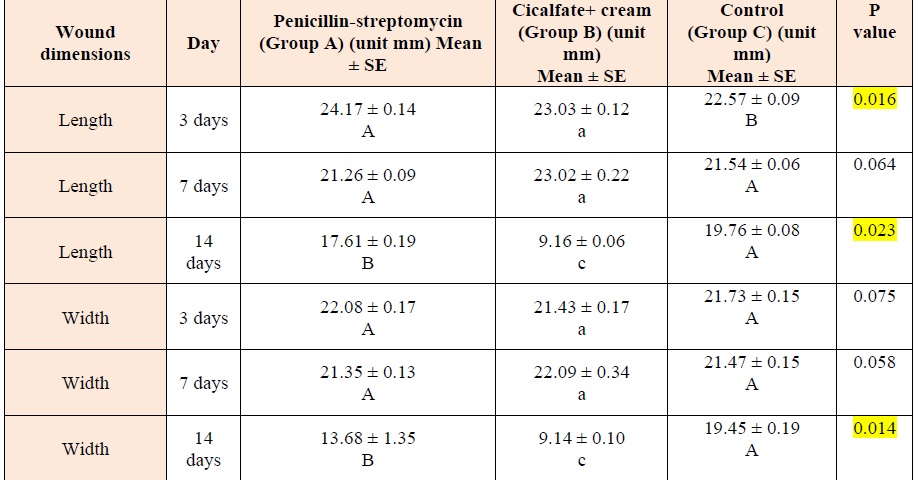
The present study was done at the College of Veterinary Medicine, Kerbala University. The purpose of the study was to examine the properties of antibiotics (penicillin-streptomycin) and a postbiotic cream (Cicalfate+ cream) on the shape of rabbits' healing processes in full-thickness skin wounds. In forty-five healthy adult bucks weighing 1.3 and 1.8 kg, full-thickness wounds measuring 2.5 x 2.5 cm were made in the dorsal back area. Intramuscular injections of xylazine hydrochloride (5 mg/kg), ketamine hydrochloride (35 mg/kg) were given very quickly (IM), along with 1 mg/kg of diazepam. In group A, one group received a daily intramuscular injection of procaine penicillin G (80,000 U/kg of body weight) along with probenecid (25 mg/kg of body weight) and streptomycin (20 mg/kg of body weight) for five days. In group B, participants applied cicalfate+ cream topically twice a day. Group C served as a control group and did not receive any treatment. On the 3rd, 7th, and 14th days after wounding, the fifteen male adult rabbits that were chosen for the morphological investigation were separated into three subgroups of five. All groups showed different rates of epidermal re- and de-generation, although the one using Cicalfate+ cream showed the fastest skin wound healing progress, according to the morphological results.
References
Liebschner MA. Biomechanical considerations of animal models used in tissue engineering of bone. Biomaterials. 2004;25:1697–714.
Bõsze Zs, Houdebine LM. Application of rabbits in biomedical research: a review. World Rabbit Sci. 2006;14:1–14.
Pearce AI, Richards RG, Milz S, Schneider E, Pearce SG. Animal models for implant biomaterial research in bone: A review. Eur Cell Mater. 2007;13:1–10.
Mapara M, Thomas BS, Bhat KM. Rabbit as an animal model for experimental research. Dent Res J. 2012;9(1).
Weledji EP. Perspectives on wound healing. Austin J Surg. 2017;4(3):1104.
Tonnesen MG, Feng X, Clark RA. Angiogenesis in wound healing. J Invest Dermatol Symp Proc. 2000;5(1):40–6.
Clark RA. Fibrin and wound healing. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;936:355–67.
Zimmermann A, Truss F. The effect of antibiotic drugs on wound-healing. Urol Res. 1974;2:73–7.
Díaz Cano JV, Argente MJ, García ML. Effect of postbiotic based on lactic acid bacteria on semen quality and health of male rabbits. Animals. 2021;11(4):1007.
Aguilar-Toalá JE, Garcia-Varela R, Garcia HS, Mata-Haro V, González-Córdova AF, Vallejo-Cordoba B, et al. Postbiotics: An evolving term within the functional foods field. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2018;75:105–14.
García-Vicente EJ, Rey-Casero I, Martín M, Pérez A, Benito-Murcia M, Risco D. Oral supplementation with postbiotics modulates the immune response produced by myxomatosis vaccination in wild rabbits. Vaccine. 2024;42:125978.
Avene. Cicalfate Sell Sheet Cream Scar Gel Hand Lips [Internet]. Available from: https://www.avene.com/media/marketing/assets/Cicalfate_Sell_Sheet_Cream_Scar_Gel_Hand_Lips.pdf
Kong HH, Segre JA. Skin microbiome: looking back to move forward. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132(3 Pt 2):933–9.
Lai Y, Di Nardo A, Nakatsuji T, et al. Commensal bacteria regulate toll-like receptor 3-dependent inflammation after skin injury. Nat Med. 2009;15(12):1377–82.
Gallo RL, Nakatsuji T. Microbial symbiosis with the innate immune defense system of the skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2011;131(10):1974–80.
Shimizu K, Ogura H, Asahara T, et al. Gut microbiota and environment in patients with major burns—a preliminary report. Burns. 2015;41(3):e28–33.
Grice EA, Kong HH, Conlan S, et al. Topographical and temporal diversity of the human skin microbiome. Science. 2009;324(5931):1190–2.
Malic S, Hill KE, Playle R, Thomas DW, Williams DW. In vitro interaction of chronic wound bacteria in biofilms. J Wound Care. 2011;20(12):569–77.
Thomson CH. Biofilms: do they affect wound healing? Int Wound J. 2011;8(1):63–7.
Albozachri JMK, Hameed FM, Al-Tomah HM, Muhammid HA. Evaluation of two general anesthetic regimes using xylazine and ketamine with atropine and diazepam in rabbits. J Univ Kerbala. 2017;15:21–30.
Pujadas R, Escriva E, Jane J, Fernandez F, Fava P, Garau J. Comparative capacity of orally administered amoxicillin and parenterally administered penicillin-streptomycin to protect rabbits against experimentally induced streptococcal endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986;29(5):909–12.
Tonnesen MG, Feng X, Clark RA. Angiogenesis in wound healing. J Invest Dermatol Symp Proc. 2000;5(1):40–6.
Clark RA. Fibrin and wound healing. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;936:355–67.
Lin PH, Sermersheim M, Li H, Lee PHU, Steinberg SM, Ma J. Zinc in wound healing modulation. Nutrients. 2018;10(1):16.
Henzel JH, DeWeese MS, Lichti EL. Zinc concentrations within healing wounds: significance of postoperative zincuria on availability and requirements during tissue repair. Arch Surg. 1970;100:349–57.
Lansdown IBG, Mirastschijski U, Stubbs N, Scanlon E, Agren MS. Zinc in wound healing: theoretical, experimental, and clinical aspects. Wound Repair Regen. 2007;15:2–16.
Rajab AM, Al-Wattar WT, Taqa GA. The roles of apigenin cream on wound healing in rabbit models. J Appl Vet Sci. 2022;7(1):1–5.
García-Vicente EJ, Rey-Casero I, Martín M, Pérez A, Benito-Murcia M, Risco D. Oral supplementation with postbiotics modulates the immune response produced by myxomatosis vaccination in wild rabbits. Vaccine. 2024;42:125978.
Ersoz M, Koc A, Ulutas PA, Serefoglu F. [Title missing]. J Biol Life Sci. 2017;8(2). [Please provide full title].
Sukandar EY, Kurniati NF, Anggadiredja K, Kamil A. In vitro antibacterial activity of Kaempferia pandurata Roxb. and Curcuma xanthorrhiza Roxb. extracts in combination with certain antibiotics against MSSA and MRSA. Int J Pharm Sci. 2016;8:108–11.
Man MQ, Hupe M, Sun R, Man G, Mauro TM, Elias PM. Topical apigenin alleviates cutaneous inflammation in murine models. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:912028.
Nam Y, Kim J, Baek J, Kim W. Improvement of cutaneous wound healing via topical application of heat-killed Lactococcus chungangensis CAU 1447 on diabetic mice. Nutrients. 2021;13:2666.
Soha B, Sahar ME, Mervet M. Assessment of the topical and systemic effects of omega-3 on oral mucosal wound healing in albino rats: a histopathological and biochemical study. Madridge J Case Rep Stud. 2018;2(1):26–31.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Academic International Journal of Veterinary Medicine

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.





