Shilajit Inhibits the Toxic Effect of Bisphenol
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59675/V318Keywords:
Shilajit, bisphenol A, and histopathological changeAbstract
The experiment was conducted at the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Kerbala, between January 3, 2025, and February 5, 2025. Special cages were used to house the rabbits during the study. A total of thirty rabbits were divided into three groups:
- G1: The Control group received water and pellets only.
- G2: Treated with Bisphenol A at a dose of 1 mL/kg.
- G3: Treated with Bisphenol A (1 mL/kg) and Shilajit (0.2 g/kg).
Biochemical analysis revealed a significant increase in liver enzymes alanine aminotransferase (ALT, IU/L) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST, IU/L) as well as in kidney function markers (urea and creatinine) in G2 compared to G1. In contrast, no significant differences were observed in G3 compared to G1 across all measured parameters.
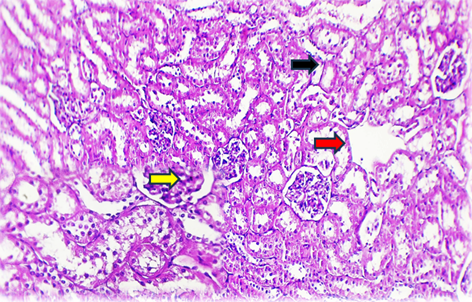
Histopathological examination of G2 livers showed bile duct hyperplasia, mononuclear cell infiltration around bile ducts, dilated blood vessels, and hydropic degeneration of hepatocytes. Perivascular aggregation of mononuclear cells, predominantly macrophages, was observed around the central vein. Renal tissue in G2 displayed glomerular tuft shrinkage, extensive interstitial mononuclear infiltration, and atrophy of surrounding renal tubules.
In G3, histopathology revealed mild mononuclear cell infiltration, including giant cells and prominent Kupffer cells in the liver. Additionally, fatty changes and apoptotic features were noted in some hepatocytes. Kidney sections showed hyaline casts, interstitial hemorrhage, and infiltration by mononuclear cells.
References
Diamante G, Schlenk D. Challenges of endocrine disruption and cardiac development. Dev Environ. 2018:319–53.
Shin BS, Kim CH, Jun YS, Kim DH, Lee BM, Yoon CH, et al. Physiologically based pharmacokinetics of bisphenol A. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2004 Dec 1;67(23–24):1971–85.
Angle BM, Do RP, Ponzi D, Stahlhut RW, Drury BE, Nagel SC, et al. Metabolic disruption in male mice due to fetal exposure to low but not high doses of bisphenol A (BPA): evidence for effects on body weight, food intake, adipocytes, leptin, adiponectin, insulin and glucose regulation. Reprod Toxicol. 2013 Dec;42:256–68.
Conroy-Ben O, Garcia I, Teske SS. In silico binding of 4,4'-bisphenols predicts in vitro estrogenic and antiandrogenic activity. Environ Toxicol. 2018 May;33(5):569–78.
Cheong A, Zhang X, Cheung YY, Tang WY, Chen J, Ye SH, et al. DNA methylome changes by estradiol benzoate and bisphenol A links early-life environmental exposures to prostate cancer risk. Epigenetics. 2016 Sep 1;11(9):674–89.
Kamgar E, Kaykhaii M, Zembrzuska J. A comprehensive review on Shilajit : what we know about its chemical composition. Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2025 Apr 3;55(3):461–73.
Mishra T, Dhaliwal HS, Singh K, Singh N. Shilajit (Mumie): current status of biochemical, therapeutic and clinical advances. Curr Nutr Food Sci. 2019 Apr 1;15(2):104–20.
Agarwal SP, Khanna R, Karmarkar R, Anwer MK, Khar RK. Shilajit : a review. Phytother Res. 2007 May;21(5):401–5.
Carrasco-Gallardo C, Farías GA, Fuentes P, Crespo F, Maccioni RB. Can nutraceuticals prevent Alzheimer’s disease? Potential therapeutic role of a formulation containing Shilajit and complex B vitamins. Arch Med Res. 2012 Nov 1;43(8):699–704.
Carrasco-Gallardo C, Guzmán L, Maccioni RB. Shilajit : a natural phytocomplex with potential procognitive activity. Int J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;2012:674142.
Aldakheel RK, Gondal MA, Alsayed HN, Almessiere MA, Nasr MM, Shemsi AM. Rapid determination and quantification of nutritional and poisonous metals in vastly consumed ayurvedic herbal medicine (Rejuvenator Shilajit ) by humans using three advanced analytical techniques. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2022 Sep 1:1–8.
Ghosal S, Lal J, Singh SK, Dasgupta G, Bhaduri J, Mukhopadhyay M, et al. Mast cell protecting effects of Shilajit and its constituents. Phytother Res. 1989;3(6):249–52.
Schepetkin IA, Xie G, Jutila MA, Quinn MT. Complement-fixing activity of fulvic acid from Shilajit and other natural sources. Phytother Res. 2009 Mar;23(3):373–84.
Jafari M, Forootanfar H, Ameri A, Foroutanfar A, Adeli-Sardou M, Rahimi HR, et al. Antioxidant, cytotoxic and hyperalgesia-suppressing activity of a native Shilajit obtained from Bahr Aseman mountains. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2019 Sep 1;32(5).
Bancroft JD, Layton C. The Hematoxylin and Eosin. In: Suvarna SK, Layton C, Bancroft JD, editors. Theory & Practice of Histological Techniques. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2013. p. 172–214.
Yamasaki K, Sawaki M, Noda S, Imatanaka N, Takatsuki M. Subacute oral toxicity study of ethynylestradiol and bisphenol A, based on the draft protocol for the 'Enhanced OECD Test Guideline no. 407'. Arch Toxicol. 2002 Mar;76:65–74.
Hassan ZK, Elobeid MA, Virk P, Omer SA, ElAmin M, Daghestani MH, et al. Bisphenol A induces hepatotoxicity through oxidative stress in rat model. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2012;2012:194829.
Kabuto H, Amakawa M, Shishibori T. Exposure to bisphenol A during embryonic/fetal life and infancy increases oxidative injury and causes underdevelopment of the brain and testis in mice. Life Sci. 2004 Apr 30;74(24):2931–40.
Mathuria N, Verma RJ. Ameliorative effect of curcumin on aflatoxin-induced toxicity in serum of mice. Acta Pol Pharm. 2008 Jan 1;65:339–43.
Tietz NW, Burtis CA, Ashwood ER, Bruns DE, Sawyer BG. Tietz fundamentals of clinical chemistry. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2001.
Melzer D, Rice NE, Lewis C, Henley WE, Galloway TS. Association of urinary bisphenol A concentration with heart disease: evidence from NHANES 2003/06. PLoS One. 2010 Jan 13;5(1):e8673.
Erden ES, Motor S, Ustun I, Demirkose M, Yuksel R, Okur R, et al. Investigation of Bisphenol A as an endocrine disruptor, total thiol, malondialdehyde, and C-reactive protein levels in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18(22):3477–83.
Poormoosavi SM, Najafzadehvarzi H, Behmanesh MA, Amirgholami R. Protective effects of Asparagus officinalis extract against Bisphenol A-induced toxicity in Wistar rats. Toxicol Rep. 2018 Jan 1;5:427–33.
Mourad IM, Khadrawy YA. The sensitivity of liver, kidney and testis of rats to oxidative stress induced by different doses of bisphenol A. Life. 2012;50:19.
Boshra V, Moustafa AM. Retracted article: Effect of preischemic treatment with fenofibrate, a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α ligand, on hepatic ischemia–reperfusion injury in rats. J Mol Histol. 2011 Apr;42:113–22.
Verma RJ, Sangai NP. The ameliorative effect of black tea extract and quercetin on bisphenol A-induced cytotoxicity. Acta Pol Pharm. 2009 Jan 1;66(1):41–4.
Roy S, Kalita CJ, Mazumdar M. Histopathological effects of Bisphenol A on liver of Heteropneustes fossilis (Bloch). Int Q J Environ Sci Ecoscan. 2011;1:187–90.
Hassan ZK, Elobeid MA, Virk P, Omer SA, ElAmin M, Daghestani MH, et al. Bisphenol A induces hepatotoxicity through oxidative stress in rat model. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2012;2012:194829.
Korkmaz A, Ahbab MA, Kolankaya D, Barlas N. Influence of vitamin C on bisphenol A, nonylphenol and octylphenol induced oxidative damages in liver of male rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 2010 Oct 1;48(10):2865–71.
Ola-Davies EO, Olukole SG, Lanipekun DO. Gallic acid ameliorates bisphenol A-induced toxicity in Wistar rats. Iran J Toxicol. 2018;12(4):11–8.
Ghezelbash B, Shahrokhi N, Khaksari M, Asadikaram G, Shahrokhi M, Shirazpour S. Protective roles of Shilajit in modulating resistin, adiponectin, and cytokines in rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Chin J Integr Med. 2022 Jun;28(6):531–7.
Kloskowski T, Szeliski K, Krzeszowiak K, Fekner Z, Kazimierski Ł, Jundziłł A, et al. Mumio ( Shilajit ) as a potential chemotherapeutic for the urinary bladder cancer treatment. Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 19;11(1):22614.
Sharma P, Jha J, Shrinivas V, Dwivedi LK, Suresh P, Sinha M. Shilajit : evaluation of its effects on blood chemistry of normal human subjects. Anc Sci Life
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Academic International Journal of Veterinary Medicine

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.





