Toxopathological and Biochemical Impacts of Albino Mice Treated with Lanxess
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59675/V315Keywords:
Lanxess, Histopathological changes, Liver enzyme, Albino mice, alkaline serum transaminase, alkaline phosphataseAbstract
Background: Lanxess (1,3-benzene dicarboxylic acid) is a safe food ingredient found in various foods and soft drinks. On the other hand, it has antifungal and antibacterial activity and is employed in the management of certain medical disorders. Additionally, it acts as an antioxidant, anti-ozonant, and anti-degradant, protecting vulcanizates against damaging external influences. This research aims to estimate the toxicity of Lanxess in the liver by measuring alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and alanine aminotransferase (AST) levels.
Materials and Methods: 20 albino mice were subdivided into two groups. The 1st group (10 mice) was administered 500 mg/kg body weight (B.w.) of Lanxess orally daily for 10 weeks as the positive control. The second group (10 mice) received PBS orally as the negative control. After the 10-week investigation, each animal was euthanized, and histological specimens from the kidney, liver, spleen, lung, and heart were collected for histopathological analysis. Blood specimens were obtained for biochemical examination.
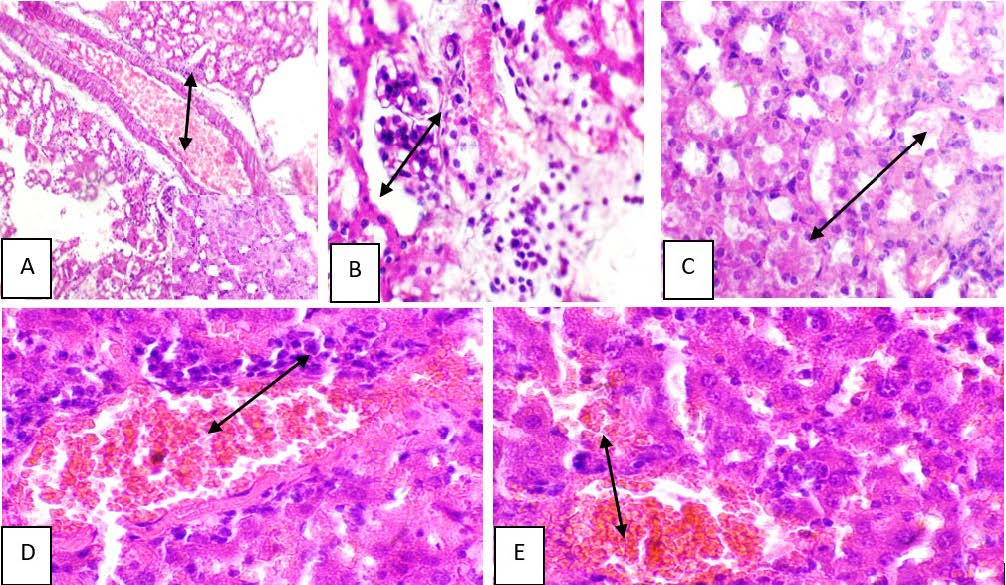
Results: The results revealed an increase in liver enzymes after 10 weeks. ALP levels were 46.10 ± 1.1, and AST levels were 59.35 ± 3.2 in the Lanxess-treated group, compared with the negative control group (ALP: 9.64 ± 2.1, AST: 6.10 ± 1.3). Examination of tissue samples showed that rats given a toxic dose of Lanxess exhibited inflammation, which included bleeding, swollen blood vessels, tissue death, scarring, and numerous lumps in the liver and other organs.
Conclusion: The results concluded that Lanxess is toxic to the liver of albino mice.
References
Khoshnoud MJ, Siavashpour A, Bakhshizadeh M, Rashedinia M. Effects of sodium benzoate, a commonly used food preservative on learning memory and oxidative stress in brain of mice. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2017;94(1):1–7.
Praphailong W, Fleet GH. The effect of pH, sodium chloride, sucrose, sorbate and benzoate on the growth of food spoilage yeasts. Food Microbiol. 1997;14:459–68.
Hejazi L, Mahboubi-Rabbani M, Mahdavi V, Alemi M, Khanniri E, Bayanati M. A critical review on sodium benzoate from health effects to analytical methods. Results Chem. 2024;9(16):101798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rechem.2024.101798
Yadav A, Kumar A, Das M, Tripathi A. Sodium benzoate, a food preservative, affects the functional and activation status of splenocytes at non cytotoxic dose. Food Chem Toxicol. 2016;88:40–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2015.12.016
Oyewole OI, Dere FA, Okoro OE. Sodium benzoate mediated hepatorenal toxicity in Wistar rat: Modulatory effects of Azadirachta indica (Neem) leaf. Eur J Med Plants. 2012;2(1):11–8. https://doi.org/10.9734/EJMP/2012/619
Lennerz BS, Vafai SB, Delaney NF, Clish CB, Deik AA, Pierce KA, et al. Effects of sodium benzoate, a widely used food preservative, on glucose homeostasis and metabolic profiles in humans. Mol Genet Metab. 2015;114(1):73–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymgme.2014.11.010
Ascib D, DincZor S, Aksu DO. Development and validation of HPLC method for the simultaneous determination of five food additives and caffeine in soft drinks. Int J Anal Chem. 2016;2016:2879406. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2879406
Brahmachari S, Jana A, Pahan K. Sodium benzoate, a metabolite of cinnamon and a food additive, reduces microglial and astroglial inflammatory responses. J Immunol. 2009;183(9):5917–27. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0803336
Maki T, Suzuki Y. Benzoic acid and derivatives. In: Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Vol A3. Weinheim: VCH Verlagsgesellschaft mbH; 1985. p. 555–68.
Akter D, Islam MM, Hossain MI, Esrafil M, Dey BP, Bari L, et al. Toxicological and histopathological effects of sodium benzoate used in commercially available fruit juice on liver and kidney tissue in mice model. Clin Nutr Open Sci. 2024;58:302–15.
Mustafa SA, Al-Rudainy AJ, Al-Faragi JK. Assessment of hydrogen peroxide on histopathology and survival rate in common carp, Cyprinus carpio L. infected with Saprolegniasis. Iraqi J Agric Sci. 2019;50(2):697–704. https://doi.org/10.36103/ijas.v2i50.669
Radam SA, Falih IB. Immunopathological and comparative study of concanavalin-A and streptococcus lyophilized antigen in immunized rats. J Adv Anim Vet Sci. 2024;12(7):1317–24. https://doi.org/10.17582/journal.aavs/2024/12.7.1317.1324
SPSS. Statistical Package for Social Science. Version 16. NC, USA: SPSS Inc; 2008.
Summaedaey AS. Experimental study of mercurical toxicosis in rats. Iraqi J Vet Med. 1989;36(2):231–43.
Sultan MS, Thani MZ, Khalaf HS, Salim AJ. Determination of some heavy metals in solid wastes from heavy water treatment station in Baghdad. Iraqi J Agric Sci. 2018;49(3):500–5.
Noorafshan A, Erfanizadeh M, Karbalay DS. Sodium benzoate, a food preservative, induces anxiety and motor impairment in rats. Neurosciences (Riyadh). 2014;19(1):24–8.
Amin KA, Abdel HH, Abdestar AH. Effect of food azo dyes tartrazine and carmoisine on biochemical parameters related to renal, hepatic function and oxidative stress biomarkers in young male rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 2010;48(10):2994–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2010.07.039
Ifemeje JC, Ezeonyemalu UE, Chukwuebuka E, Olisah MC, Ifemeje MO. Effects of four different food additives on the oxidative stress markers of Wistar albino rats. Int Ann Sci. 2020;9(1). https://doi.org/10.21467/ias.9.1.46-51
Forouzan K, Hossein K, Masood H, Marzieh R. Effect of sodium benzoate on liver and kidney lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzymes in mice. J Rep Pharm Sci. 2019;8(2):217–23. https://doi.org/10.4103/jrptps.JRPTPS_68_18
Chih RL, Karim B, Beata K. Impaired alveolar re-epithelialization in pulmonary emphysema. Cells. 2022;11(13):2055. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11132055
Modi KK, Jana M, Mondal SPK. Sodium benzoate, a metabolite of cinnamon and a food additive, upregulates ciliary neurotrophic factor in astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. Neurochem Res. 2015;40(11):2333–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1723-x
Kaltschmidt B, Kaltschmidt C, Hofmann TG, Hehner SP, Droge W, Schmitz ML. The pro- or anti-apoptotic function of NF-κB is determined by the nature of the apoptotic stimulus. Eur J Biochem. 2000;267(12):3828–35. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01421.x
Gonzalez KC, Sagebin FR, Oliveira PG, Glock L, Thiesen FV. A retrospective study analysis of urinary hippuric acid levels in occupational toxicology exams. Cien Saude Colet. 2010;15 Suppl 1:1637–41. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1413-81232010000700075
Beyoglu D, Idle JR. The glycine deportation system and its pharmacological consequences. Pharmacol Ther. 2012;135(2):151–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2012.05.003
Khidr B, Makhlouf M, Ahmed S. Histological and ultrastructural study on the effect of sodium benzoate on the liver of adult male albino rats. Assiut Univ J Zool. 2012;41(1):11–39.
Bakar E, Aktac T. Effects of sodium benzoate and citric acid on serum, liver and kidney tissue total sialic acid levels: An ultrastructural study. J Appl Biol Sci. 2014;8(2):9–15.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Academic International Journal of Veterinary Medicine

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.





